Artificial Intelligence | Explanation, Examples & Types
Who Invented & Created Artificial Intelligence?
The term “Artificial Intelligence” was first used in 1956 by John McCarthy, a computer scientist, during the Dartmouth Conference. This conference is widely considered to be the birthplace of AI as a field of study. He defined “Artificial Intelligence as the science and engineering of making intelligent machines.”
What is Artificial Intelligence?

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a technology that allows machines to carry out tasks that usually need human intelligence. In recent years, AI has advanced significantly, leading to the creation of machines and robots used in various fields like healthcare, robotics, marketing, and business analytics.
Everyday Presence of AI
Many AI applications are so common that we often don’t recognize them as AI. We tend to imagine AI as robots doing our chores, but AI is integrated into our daily lives in more subtle ways.
For example, Google provides accurate search results and Facebook tailors your feed based on your interests, both thanks to AI.
Clarifying AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning
It’s important to understand the differences between AI, machine learning (ML), and deep learning (DL).
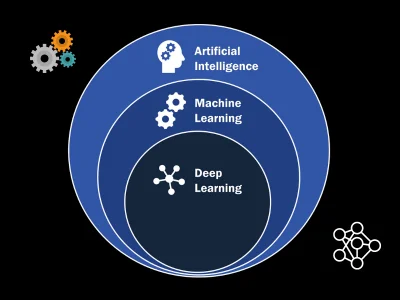
AI performs tasks that require human intelligence, while machine learning (ML) is a subset of Ai and deep learning (DL) is a further subset of machine learning (ML) as shown in the diagram below.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)

AI involves creating machines that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as recognizing speech, learning from experience, planning, and problem-solving.
Machine Learning (ML)

ML is a branch of AI where machines learn from data without being explicitly programmed. It focuses on developing algorithms that can improve automatically through experience.
Examples include email spam filters, recommendation systems, and image recognition.
Deep Learning (DL)

DL is a subset of ML that uses artificial neural networks with many layers (deep neural networks) to learn from large amounts of data.
DL has revolutionized fields such as computer vision and natural language processing, achieving remarkable accuracy in tasks like image and speech recognition
Fields Covered by AI
AI is not limited to machine learning and deep learning. It also includes areas like natural language processing, object detection, computer vision, robotics, and expert systems.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can generally be classified into three main types based on its capabilities and functionalities, following are the three main types:
ANI Vs AGI Vs ASI
| Feature | Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) | Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) | Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI) |
| Capability | Performs a specific task very well | Performs many tasks like a human | Surpasses human intelligence in all aspects |
| Current Status | Widely available | Theoretical | Hypothetical |
| Example | Self-driving car, spam filter, facial recognition software | (Does Not Exist yet) | (Does Not Exist yet) |
| Learning | Learns to perform a specific task through data and algorithms | Learns and adapts to new situations like a human | Goes beyond human learning capabilities |
| Consciousness | No | Debated | Possible but unknown |
| Applications | Manufacturing, healthcare, customer service | (Not applicable yet) | Potentially limitless |
| Benefits | Increased efficiency, automation of tasks | Enhanced problem-solving, improved decision-making | Unforeseen positive outcomes |
| Risks | Job displacement, bias in algorithms | Unforeseeable consequences | Loss of human control |
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), also called weak AI, is a form of artificial intelligence that specializes in performing a specific task or a limited range of tasks.
Unlike humans, who can perform a wide variety of activities, ANI is designed to excel at one particular function. It is transforming the world rapidly!
Following are some of the examples:
Alexa
Face Verification on iPhones
This feature uses AI to recognize and verify users’ faces, allowing secure access to the device and specific apps.
Tesla’s Autopilot
Tesla’s self-driving feature uses AI to navigate roads, detect obstacles, and respond to traffic conditions, enhancing driving safety and convenience.
Sophia the Humanoid
Developed by Hanson Robotics, Sophia can hold conversations, display a range of facial expressions, and answer questions, showcasing advanced social interactions within a defined scope.
Google Maps
Uses AI to analyze traffic data and provide real-time route updates, as well as to offer accurate directions by understanding and predicting user behavior and patterns.
Email Spam Filters
AI algorithms scan incoming emails to identify and filter out spam messages based on patterns and content analysis, ensuring users receive relevant emails.
Online Customer Support Chatbots
Many websites use AI-powered chatbots to interact with customers, answer common queries, and provide support, reducing the need for human intervention in basic customer service tasks.
Recommendation Systems
Platforms like Netflix and Amazon use AI to analyze user preferences and behaviors, recommending movies, TV shows, or products tailored to individual interests, improving user experience and engagement.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
Known as strong AI, AGI aims to perform any intellectual task that a human can. Currently machines do not possess the ability to think and reason like humans.
Experts debate whether AGI is achievable or desirable, with notable figures like Stephen Hawking warning about the potential risks.
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI)
This refers to a future stage where AI surpasses human intelligence. It remains a hypothetical scenario often depicted in science fiction. Tech leaders like Elon Musk predict that ASI might emerge by 2040.
Examples of AI in Real Life
Finance

JP Morgan’s Contract Intelligence Platform
Utilizes AI to swiftly analyze extensive legal documents, extracting crucial data points and clauses with accuracy, a task that would be time-consuming and prone to human error if done manually.
Healthcare

IBM Watson
Deployed across 230+ healthcare institutions, Watson leverages AI to sift through vast amounts of medical data, aiding in the diagnosis and personalized treatment plans for patients, including rare conditions like certain types of leukemia.
Google’s AI Eye Doctor
Enhances healthcare by using AI to examine retina scans for signs of diabetic retinopathy, a condition that can lead to blindness if not detected early, thereby assisting in proactive patient care and management.
Social Media

Implements AI for face verification, ensuring secure account access, and content personalization by analyzing user preferences and behavior to tailor newsfeeds and advertisements.

Utilizes AI to detect and filter out hate speech and terrorist language from tweets, helping maintain a safe and positive online environment while respecting freedom of expression.
Search Engines
Google Predictive Search
Enhances user experience by employing AI algorithms that predict search queries based on past searches, location, and demographic data, providing relevant suggestions even before the user finishes typing.
Search Engines
Siri, Alexa, Cortana
These virtual assistants leverage AI to perform tasks like setting reminders, playing music, and controlling smart home devices through voice commands, enhancing convenience and efficiency in daily activities.
Google Duplex
Mimics human interaction by using AI to make phone calls and book appointments on behalf of users, showcasing advanced natural language understanding and conversation capabilities.
Self-Driving Cars
Tesla’s Autopilot
Integrates AI for autonomous driving, utilizing sensors and cameras to detect and navigate around obstacles, interpret traffic signals, and maintain safe driving conditions without direct human input, contributing to safer and more efficient transportation systems.
The Future of AI
AI has seen exponential growth since its inception in the 1950s. Its applications span machine learning, deep learning, neural networks, natural language processing, and more.
As AI continues to evolve, it’s essential to consider its potential impact on our lives and how we can prepare for a future where AI plays an even more significant role.


